“DARWIN WAS WRONG”
(A Study in Probabiliti es)
es)
A book report. Author and copyright holder I.L.Cohen. Copyright date 1984. My copy was printed in the USA in 1985’
While not a new work by far, it is not outdated because the philosophies and arguments of the book are timeless.
Dedication: This book is dedicated to those trained to think scientifically and who are not afraid to reach conclusions dictated by their objective logic-
The introduction addresses the spirited debate that has raged for decades between evolutionists and creationists. In his words;”the latter had a simple base on which they relied: the Old Testament. The God of the Hebrews had stated that God created mankind. That particular statement was sufficient evidence for the creationists to accept it at face value, “on faith”, and erect all subsequent arguments.
The evolutionists, however, could not accept a mere statement as the basis for one’s conclusions and beliefs. There had to be a scientific explanation, -
-
a) At the beginning there was only heaven and Earth.
b) Life started spontaneously from inanimate inorganic matter.
c) A simple single cell first formed from interactions of pressures, water (perhaps mud), chemicals, temperatures, etc. Theses first forms of life were to be found in water.
d) That simple cell multiplied and split, forming newer forms of life: 2-
e) With the passing of untold millions of years, these organisms developed into fish with gills; additional millions of years later some fish moved onto dry land.
f) -
k) Change from one stage to the next was achieved by certain methods:
1) Evolution took place in gradual but imperceptibly small improvements, from stage to stage.
2) Species improved through survival of the fittest individuals.
3) More advanced species were created through the genetic transmission of acquired physical characteristics.
4) Haphazard mutations created a variety of species and organs.
5) This process was steady and continuous over untold millions of years.
-
During the years that followed fossils and skeletal remains were anxiously sought since they were the crucial evidence that would demonstrate all the postulated intermediate stages of development. Unfortunately, the many fossils dug apparently indicated the contrary: halfway stages were the preponderate exception not the rule. Geological strata, going back hundreds of millions of years, almost invariably gave us faunas and floras of fully developed orders, families, genera and species. Once such an assemblage was located in its strata, individual species persisted unchanged during the hundreds of millions of years of their known existence. -
To remedy this unexpected contradiction of a cornerstone of evolutionary theory, a new concept was introduced, punctuated equilibria. -
With time, and as newer findings frustrated the awaited proof, we reached a stage of polarization between evolutionists and creationists. Positions became frozen and degenerated into a blind, stubborn repetition of old arguments and name calling. On the one hand the creationists were clinging to their one sentence in the Bible and insisting that creation was a fact because God said so. On the other hand, evolutionists were continually patching up the original theory and calling on convoluted logic, couched in elegant, educated terminology, to create an aura of science.
In the 1950s, while this indecisive tug of war was still being waged, a momentous event occurred-
At that moment, when the DNA/RNA systems became understood, the debate between creationists and evolutionists should have come to a screeching halt. We now had a precise mechanistic tool with which to measure and evaluate our concepts of evolution.
In the final analysis the whole argument of this book will boil down to answer a very basic question:
Are the millions of species on earth the result of accidental, haphazard arrangements and rearrangements (mutations) of DNA molecules that took place without infusion of outside intelligence – or are they attributable to purposeful, predetermining intelligence?
The book invites the reader to continually ask a very simple question each time an evolutionary argument is being evaluated.
If we translate the specific occurrence into DNA nucleotides and apply mathematical probability principles to the argument at hand, what kind of probability figure do we obtain?
The conclusions submitted in this book have not been reached on the basis on any religious beliefs -
In chapter 2 the author discusses the concept of probabilities based on mathematics. He concluded that any scenario who’s mathematical complexity would equal or exceed an example of 84 balls, equally divided in 4 different colors, that need to be arranged in any specific sequence by random processes, becomes a mathematical impossibility. The likelihood of that happening by accident is a calculable possibility of 2.08X10-
In chapter 3 he gives a general description of the composition of the living cell with its components and organelles to give a glimpse of it’s complexity. What was thought by Darwin to be only a very simple sack of chemicals, but has been discovered to be complex beyond imagination, and beyond the scope of ability of even the most knowledgeable of modern scientists to duplicate.
In chapter 4 he describes the marvels of the DNA/RNA. The information and control segment of the machine of life. On page 48 he shows a schematic describing the protein building apparatus of the cell. He explains this process as follows-
l) The mRNA (messenger RNA) brings in from the DNA a coded sequence of nucleotide message. 2) This mRNA seeks and attaches itself to a ribosome. While passing through it, it allows the ribosome to "read" the sequence of C-
See next page
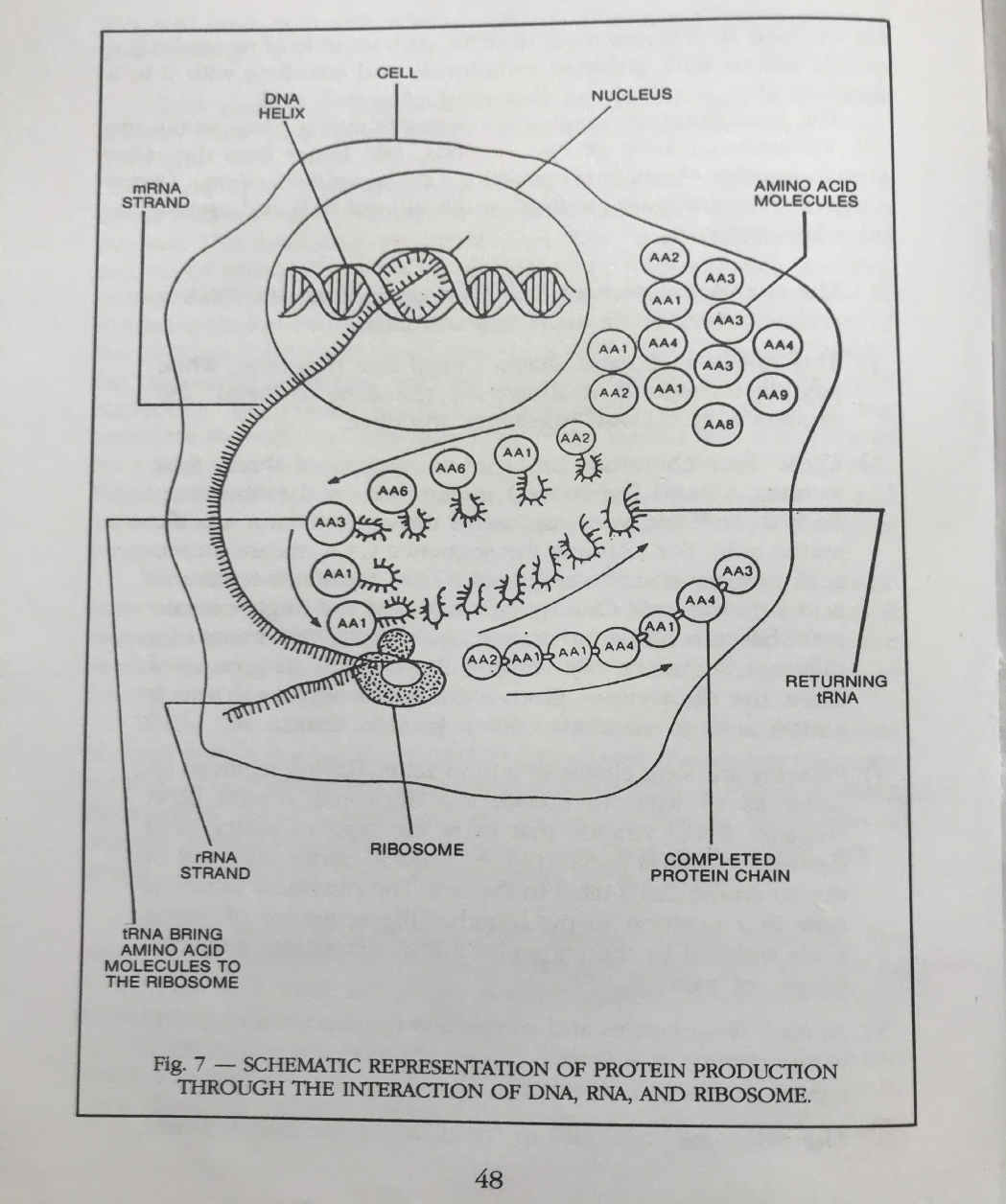

He describes the process whereby the DNA strand is duplicated when an organism adds cells in growth or in reproduction. This amazing process is the exact opposite of evolutionary process as it ensures the reproduction of the same kinds rather than producing the missing links that evolution requires. In chapter 6 he addresses purposefulness in the genetic commands. He highlights the fact that not only do the genetic letters code for specific amino acids, there are actually 3 letter stop and go signals as well, clearly telling the ribosome (protein factory) when to start and stop building a protein. Nothing is left to chance and random processes rather the design and precision goes way beyond the intelligence level of the computer scientist. In chapter 7 he asks, “What does it all mean?” Here he carefully makes his argument that evolutionary mutations and natural selection must necessarily be understood in the language of the DNA. That means that for an animal to gain fins like a fish or wings like birds would require the deliberate placement of untold numbers of additional nucleotides or genetic letters into the DNA strand to facilitate that growth. What part of the life machine would give those orders? Also where would the information be added, at the beginning or end; in the middle? Since adding an organ would affect many other parts of the organism as well, could the random process evolution produce the precision required to insert the new instructions, with appropriate stop and go signals to avoid destroying the existing organism in order to produce an improved one?
It must be remembered that when Darwin imagined mutations and natural selection he had no idea of the DNA, nor could he have realized that mutations would necessarily have to be genetic mistakes. When he coined those terms, the terms covered vast areas of science that he and his contemporaries knew nothing about.
Does Science Prove Evolution?